My thinking about what platforms and ecosystems look like in the online media world seems to evolve constantly. It has certainly become more clear, bigger and more nuanced the last 2 years or so, but the language to describe a media platform feels very unfinished still.
It may be that the word ‘platform’ is throwing off conflicting ideas of what exists in my head. If you ask 10 people to define a platform you’ll get 10 different answers.
You can think of a platform in several different ways. There’s the functional role it serves. You can talk about the ecosystem around it. Some explain it in terms of the pieces and how they interact. It can also be an abstract concept or more of a strategic view of things.
Blogger (and conspiracy theorist) Kid Mercury has a paper of sorts defining platforms in terms of the strategies that they serve and their relationship to products, particularly in the Web 2.0 context:
“Products are “things” (goods, services, experiences, etc) that are sold; platforms are the intermediaries that deliver products. True to Yin/Yang form, the two are complementary yet opposing as well; platforms cannot exist without products, and products need platforms to be put into context and to be found.”
Wikipedia has several entries on platforms including “computing platforms“, “political platforms” and “platform shoes“:
“Platform often describes the set of hardware components that make up the computer itself, that the software is written to target (often just described as “written for an architecture”).”
Auto manufacturers initiated platform strategies in the 1960’s and ’70’s to improve several aspects of their processes:
“Vehicle platform-sharing combined with advanced and flexible-manufacturing technology enables automakers to sharply reduce product development and changeover times, while modular design and assembly allow building a greater variety of vehicles from one basic set of engineered components. Many vendors refer to this as product or vehicle architecture.”
Similarly, John Hagel and John Seely Brown noted how platform design in auto manufacturing in Asia has enabled amazing efficiencies in their 2006 paper “Connecting Globalization & Innovation: Some Contrarian Perspectives“:
“Honda’s share of Vietnam’s motorcycle market, for instance, dropped from nearly 90 percent in 1997 to 30 percent in 2002. Japanese companies complain about the “stealing†of their designs, but the Chinese have redefined product architectures in ways that go well beyond copying, by encouraging significant local innovation at the component and subsystem level. “
David S. Evans, Andrei Hagiu and Richard Schmalensee go into great detail about various approaches to platforms taken by companies like Microsoft and Apple in their book “How Software Platforms Drive Innovation and Transform Industries.” They explained several models for how platform businesses work:
“In a multisided strategy, the software platform mainly facilitates inter-actions between the sides of the platform (particularly applications vendors and end users). In a single-sided (or merchant) strategy, the platform either produces the complementary products itself or buys them and resells them to end users. “
The book jumps from strategy down to specific detail such as this bit about how to develop relationships with customers:
“In the case of the software platforms we have examined, even the weakest relationships are far deeper than the arm’s-length relationships one sees in many one-sided industries. Software platforms can’t have direct relationships with the thousands of small developers, hardware makers, and peripheral device makers. Yet they document and make APIs available to developers, provide interface information to hardware and peripheral makers, and make sure their platforms have the relevant drivers for the peripherals. And they develop relationships through large developer conferences and small focus groups that bring some of these smaller players together. At the other extreme, software platforms often have deep relationships with several larger partners. These relationships involve regular exchange of information and joint work on defining new standards and specifications. They may also involve joint investments in product development or marketing.”
Thomas Eisenmann of Harvard Business Review has done some interesting work addressing the network effects of the modern media platform in his paper called “Platform-Mediated Networks: Definitions and Core Concepts“. He uses Visa’s and Microsoft’s XBox platforms to compare and contrast different methods for creating network effects. He talks about how a jointly sponsored platform like Visa’s leverages more complicated but more scalable relationships vs the single-proprietor platform like Microsoft’s which has lots of dependencies.
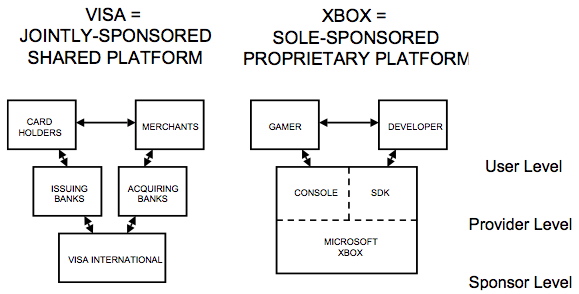
He builds on this view in his follow up work with Geoffrey Parker and Marshall Van Alstyne for MIT. In “Network Platforms – Core Concepts” he builds network effects as a necessary component of a platform:
“A “Network platform†is defined by the subset of components used in common across
a suite of products (Boudreau, 2006) that also exhibit network effects. Value is exchanged among a triangular set of relationships including users, component suppliers (co-developers), and platform firms.”
They spell out some of the trickier issues the platform organizations need to consider such as channel conflict:
“Platform providers must determine how much of the value created through network
interactions they should seek to capture and from which users. consider who adds the most value. A bigger network served by a single platform can create more value in aggregate, but users may worry that a dominant platform provider will extract too much value. Likewise, when the participation of a few large users is crucial for mobilizing a network (e.g., movie studios vis-a-vis new DVD formats), conflict over the division of value between platform providers and “marquee†users is common.need to give in order to get. Controlling most of a multi-billion dollar business is better than controlling all of a million dollar business. “
Just having a platform and a platform strategy is not enough. There are organizational requirements that make it possible to drive a platform business. Kid Mercury adds some insight into the ways in which organizations must institutionalize capability creation to serve platforms rather than functional hierarchy to serve products:
“There can be no long value chains where each employee is a rung in a ladder, with all the value ultimately flowing to the top. Such hierarchical organizations are essentially immobile by design; they are not capable of creating new capabilities because everyone in the vertical hierarchy is participating in a way that only serves the existing value chain. This is great for incremental innovations, as such a structure essentially institutionalizes the process of adding more value to existing value chains. It is not so effective, though, for creating new value chains.”
I’m looking for more views on platform strategies and ecosystems, so please comment below if you have any favorites. I haven’t found as much dialog and literature as I’d like.
I suppose all this goes hand-in-hand with some of the discussion around designing for growth. Maybe I’m alone here, but I’m more interested than ever before in this old magazine idea.
Comments are closed.